The hobo house spider is actually a funnel web spider. This is because it builds webs that take on the appearance or shape of a funnel. It is thought to have been first introduced sometime before 1930 to North America via agriculture shipments to Seattle. Since then, the spider has thrived in American urban cities and is now spread over much of the Pacific Northwest including parts of Canada.
This spider is somewhat large and their bite is very painful. Much like the brown recluse, their venom causes lesions and for this reason bites are often misdiagnosed. The hobo spider was most notably called “the aggressive house spider” due probably to its bite and speed. This title was later dropped after much study proved this was not a suitable moniker to describe this arachnid. That said, the hobo spider is the leading cause of serious spider bites in the Northwest.
What Does The Hobo Spider Look Like?
Identification of the hobo house spider is difficult because most of it would require the use of a magnifying glass. Mature female hobo spiders are 3/8-5/8 in long, and male is slightly smaller in body length. It is commonly reported that identification marks include chevron markings on the arachnid’s abdomen. These chevrons, ‘V’ shaped marks always point to the head of the spider. This however is also seen on other spiders so it can’t be relied on 100%. Also this spider lacks colored bands where the leg joints meet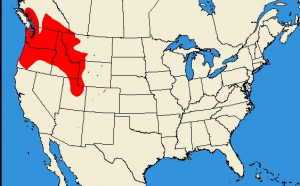 and two distinct stripes (longways) on their cephalothorax but again, this is not exclusive to the hobo spider. The quickest way would be to look at its eyes. (same for the brown recluse) The hobo spider has 8 eyes in two almost straight rows. That said; To positively ID this spider you should consult an expert.
and two distinct stripes (longways) on their cephalothorax but again, this is not exclusive to the hobo spider. The quickest way would be to look at its eyes. (same for the brown recluse) The hobo spider has 8 eyes in two almost straight rows. That said; To positively ID this spider you should consult an expert.
Is It Aggressive? Is It Poisonous?
Experts are currently in a disagreement whether or not the hobo house spider is aggressive and has enough venom to match the toxicity of the bite of a brown recluse spider. If left alone there are no substantiated cases where this spider has sought out a human to bite. However, if accidental contact is made or if the spider is protecting its egg sacs, bites can occur.
Some scientists have suggested that its bite can induce necrosis on humans based on tests done on rabbits, while others strongly dispute that claim. Studies in Canada claim no such dermal necrosis is caused but several cases do seem to exist that dispute this. In a normal healthy human however, hobo bites are not believed to be fatal. What has been confirmed though is that the bite of a hobo house spider can cause extreme pain in the immediate area.
Can I Treat My Home
As with any spider, it is best to leave the hobo house spider alone in its web. They will bite to protect themselves or their eggs if you get too close to their haunt, and control through insecticides (if needed) should be done at a distance away from the web. Most residual insecticides are not known to be that effective on spiders, although wettable powders have been used with positive outcomes. Injecting dusts, aerosols or other quick knock down products into the nest area will give best results.
 To prevent the hobo house spider from living on your home, regularly clean areas in which it is likely to live in like corners of your home, flower vases, the attic and many others. If you see a web, use a broom or vacuum cleaner to remove it. The vacuum cleaner may be preferred because it can remove any egg sacs that carry future hobo house spiders.
To prevent the hobo house spider from living on your home, regularly clean areas in which it is likely to live in like corners of your home, flower vases, the attic and many others. If you see a web, use a broom or vacuum cleaner to remove it. The vacuum cleaner may be preferred because it can remove any egg sacs that carry future hobo house spiders.




